Health
Acute and chronic inflammation: causes, symptoms and treatment

What is inflammation? Let's look at the causes, symptoms, and treatments of inflammation, as well as their classifications.
Nonspecific inflammation, inflammation it can affect anyone. Not only that, it can be an acute and chronic disease and, consequently, evolve in different ways and with almost opposite symptoms. Let's see what are the classifications of the pathology, the causes, the treatment and the most effective treatments.
Phlogosis: what is it?
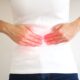
Inflammation is nothing more than an inflammation that the human organism automatically puts in place when it feels in danger. Specifically, it acts in response to cell damage caused by agents of various kinds (physical, chemical or biological). In doing so, and thanks to the intervention of the cells of the immune system, it starts the so-called repair process. Among the most common causes of inflammation are:
- physical trauma (such as: stab wounds, excessive muscle stress, shock and impact trauma);
- burns ;
- freezing;
- radiation;
- acids;
- poisons;
- alkali;
- oxidizing agents
- microorganisms (such as: virus, fungal and bacterial infections);
- allergic reactions;
- autoimmune diseases (such as: rheumatoid arthritis, some forms of hepatitis, diabetic neuropathy and gastritis).
The inflammation, mild or intense, manifests itself in different ways according to the triggering cause and the type of inflammation . From redness to swelling, through increased heat and body temperature and pain: these are just some of the possible symptoms. Based on the latter, it is classified in acute or chronic inflammation.
View this post on Instagram
Nonspecific phlogosis: treatment and care
Whether the inflammation is intense or mild, it can be acute or chronic. In the first case, it is an inflammation that resolves within a few days. It usually comes suddenly and mostly involves blood vessels. When it is chronic , on the other hand, it is a consequence of the acute phase not completely resolved. Therefore, the duration is greater and the tissues are also involved. Not only that, two types of chronic inflammation can also be distinguished: granulomatous and interstitial inflammation. As you may have easily guessed, we cannot speak of a single cure. However, the aim of the treatment is to promote the cellular repair process and reduce the negative effects.
Riproduzione riservata © - WT